Retirement Planning With Healthy Life Expectancy In Mind
Filed in: Pensions
01 April 2025
Healthy Life Expectancy
Key Points Summary
- Healthy Life Expectancy (HLE) vs. Traditional Planning: While traditional retirement planning focuses on overall life expectancy, HLE represents the years one can expect to live in good health without limiting disabilities. This distinction is crucial as there's typically a 9-12 year gap between life expectancy and healthy life expectancy.
- Financial Implications of Health Phases: Retirement spending follows distinct patterns based on health stages, typically higher discretionary spending during healthy years followed by increased healthcare costs during years of declining health. Planning should account for this shifting allocation of resources.
- Strategic Investment Approach: HLE data should guide contribution timing, portfolio construction, and withdrawal strategies. This includes accelerating savings during peak earning years, adjusting investment time horizons based on expected health phases, and potentially front-loading discretionary spending.
- Beyond Financial Planning: HLE-informed retirement planning leads to more realistic expectations, better risk management, enhanced legacy planning and improved family communication about potential caregiving needs and financial arrangements.
In the world of retirement planning, we often focus on a single number: the age we plan to stop working. Traditional financial advice centers around accumulating enough wealth to support ourselves from that magic retirement age until our expected death. However, this approach overlooks a crucial factor that significantly impacts retirement satisfaction, the Healthy Life Expectancy (HLE).
Understanding and incorporating HLE into retirement planning can dramatically change how we prepare for our later years and ultimately lead to more fulfilling retirements.
What is Healthy Life Expectancy?
Healthy Life Expectancy (HLE) refers to the number of years a person can expect to live in good health, free from disease or disability that limits daily activities.
Unlike overall life expectancy, which simply measures how long someone is expected to live, HLE specifically focuses on the quality of those years. It represents the period during which an individual maintains functional abilities and can fully engage in desired activities without significant health-related limitations.
The World Health Organisation defines HLE as "the average number of years that a person can expect to live in 'full health' by taking into account years lived in less than full health due to disease and/or injury."
Healthy Life Expectancy vs. Mortality Rates: Understanding the Distinction
While closely related, Healthy Life Expectancy and mortality rates measure fundamentally different aspects of population health:
• Mortality Rates track the frequency of death within a population during a specific time period. They answer the question: "How long will people live?" These rates help calculate overall life expectancy, the average length of life for individuals in a population.
• Healthy Life Expectancy measures the quality of those years by estimating how many will be spent in good health. It answers a different question: "How long will people live in good health?" This metric acknowledges that not all years of life are equal in terms of functional capacity and quality.
The gap between overall life expectancy and HLE represents years spent living with health conditions that impact quality of life. This distinction is crucial for retirement planning because the activities, expenses, and needs of retirees change significantly depending on their health status.
Why Healthy Life Expectancy Matters for Retirement Planning
Despite its importance, HLE remains largely overlooked in conventional retirement planning. The reasons for this oversight and its significance include:
• Lifestyle Planning Beyond Finances
Traditional retirement planning focuses almost exclusively on financial readiness, yet the quality of retirement years depends heavily on health status. Knowledge of one's potential HLE allows for more realistic planning of retirement activities, housing needs, and general lifestyle expectations.
• Healthcare Cost Projections
Healthcare costs represent one of the largest expenses in retirement, and these costs accelerate significantly during years of poor health. Understanding the potential gap between life expectancy and HLE enables more accurate forecasting of healthcare expenses.
• Income Distribution Strategies
HLE data can inform when and how to draw from different retirement accounts. For example, retirees might choose to front-load discretionary spending during their healthy years and reserve more conservative assets for later-life healthcare needs.
• Geographic and Housing Decisions
Knowledge of potential health limitations might influence decisions about retirement location, housing type, and proximity to healthcare facilities or family support systems.
• Legacy Planning
Understanding HLE impacts inheritance planning and charitable giving strategies, allowing individuals to make more informed decisions about asset distribution during or after their lifetime.
• Statistical Overview: Healthy Life Expectancy vs. Life Expectancy
The following table provides a comparison of life expectancy and healthy life expectancy across different regions and countries:
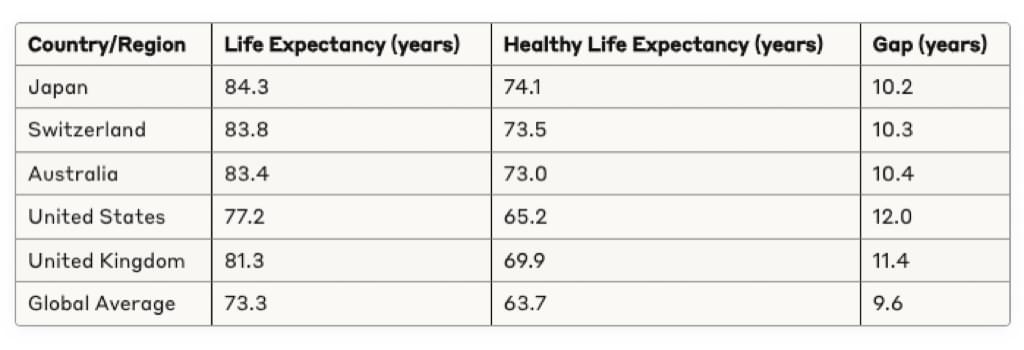
The above statistics reveal several important patterns:
1. Even in countries with the highest life expectancies, individuals can expect to spend approximately a decade in sub-optimal health.
2. The gap between life expectancy and HLE varies significantly across countries, influenced by healthcare systems, lifestyle factors, and social determinants of health.
3. Women typically have longer life expectancies than men but often experience more years of disability, resulting in a larger gap between life expectancy and HLE.
Incorporating Healthy Life Expectancy into Retirement Planning
Contribution Strategies
Understanding HLE should influence how individuals approach saving for retirement particularly in respect of the reducing pay days left to retirement:
1. Accelerated Savings During Peak Earning Years: Knowing that health may decline earlier than expected motivates maximising contributions during peak earning years.
2. Health-Specific Savings Vehicles: Greater emphasis on health savings accounts (HSAs) and long-term care insurance when the data suggests a significant gap between life expectancy and HLE.
3. Work Flexibility Planning: For those with family health histories suggesting earlier health challenges, planning for reduced work hours or career transitions before traditional retirement age might be prudent.
Investment Portfolio Construction
HLE considerations should impact investment allocation and risk management:
1. Time Horizon Adjustments: Rather than using overall life expectancy to determine investment time horizons, using HLE provides a more realistic framework for when certain assets might need to be liquidated.
2. Liquidity Planning: Ensuring sufficient liquidity during healthy years for lifestyle activities and experiences, while maintaining growth components for later healthcare needs.
3. Risk Allocation Phases: Implementing a risk management approach that aligns with anticipated health phases rather than simple age brackets.
Future Income Requirements
HLE significantly impacts both the amount and timing of retirement income needs:
1. Front-Loaded Discretionary Spending: Many retirees find their discretionary spending (travel, hobbies, leisure activities) concentrates in early retirement years when health permits active engagement.
2. Healthcare Expense Curves: As health declines, healthcare expenses typically increase, requiring a shift in budget allocation from discretionary to necessary medical expenses.
3. Support and Assistance Costs: The final phase of retirement often involves significant costs for assistance, whether through in-home care, assisted living facilities, or nursing homes.
4. Geographic Flexibility: Health often dictates where retirees can live, with healthy years offering maximum flexibility and later years potentially requiring proximity to medical facilities or family caregivers.

Benefits of HLE-Informed Retirement Planning
Realistic Expectations and Greater Satisfaction
By acknowledging health limitations that may occur earlier than expected, retirees can develop more realistic expectations and prioritise experiences accordingly. This awareness helps prevent the disappointment that comes from deferring important life experiences until health no longer permits them.
More Accurate Financial Forecasting
Traditional retirement planning often underestimates healthcare costs and overestimates the duration of active retirement. HLE-informed planning provides a more accurate financial roadmap by accounting for changing needs throughout retirement phases.
Better Risk Management
Understanding potential health limitations allows for more effective risk management strategies, such as earlier long-term care planning particularly for those that may have suffered a critical illness or housing modifications before they become urgent necessities
Enhanced Legacy Planning
With clearer expectations about healthcare needs and expenses, retirees can develop more accurate predictions about their legacy potential and make arrangements accordingly.
Improved Family Communication
HLE-informed planning facilitates more meaningful family discussions about expectations, potential caregiving needs, and financial arrangements, reducing stress during health transitions.
Conclusion
Retirement planning that considers only financial metrics and overall life expectancy presents an incomplete picture. By incorporating Healthy Life Expectancy into retirement strategies, individuals can develop more nuanced, realistic plans that acknowledge the different phases of retirement and their associated needs.
The gap between life expectancy and HLE represents years that require specialised planning for healthcare, assistance, and modified lifestyle expectations. By confronting this reality early in the planning process, future retirees can make better decisions about savings rates, investment allocations, and lifestyle priorities.
As our understanding of longevity continues to evolve, the financial services industry should move beyond simplistic retirement age targets and embrace planning frameworks that acknowledge the critical importance of health throughout retirement. Only then can we truly prepare for retirement in a way that maximises both financial security and quality of life during our later years.
For anyone developing a retirement strategy, the question should not simply be "Do I have enough?" but rather "Do I have the right resources, allocated appropriately, to support my needs and goals throughout the different health phases of my retirement?"
By considering "Healthy Life Expectancy" in retirement planning conversations, we can help ensure that retirement years are not just financially secure but genuinely fulfilling.
