American Credit Card Delinquency
Filed in: Momentum |Investment |Pensions |Savings |Economy
30 May 2024
Understanding the Rise in US Credit Card Delinquencies & Chart Analysis
Key Points Summary
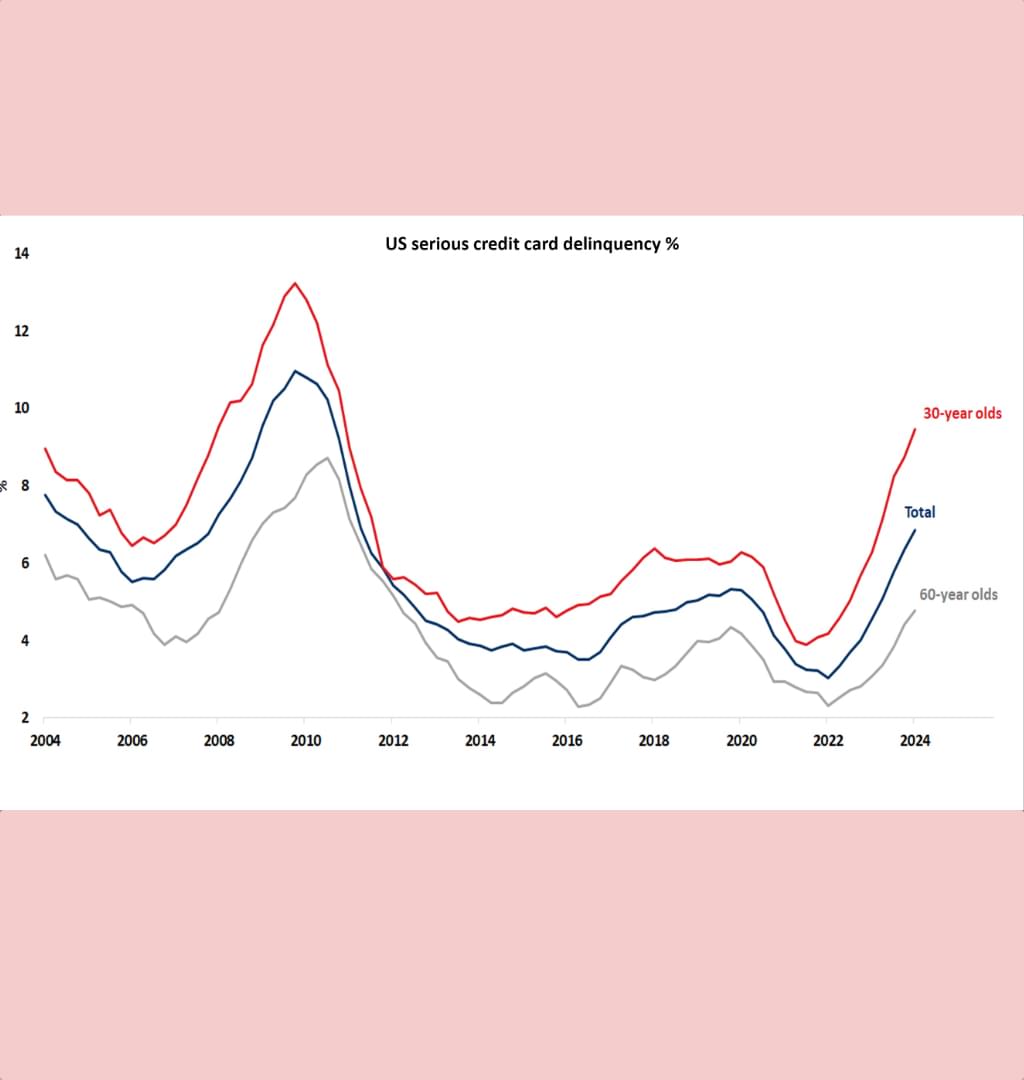
- Rising Delinquencies: US credit card loans 90 days or more overdue increased from 3% in Q1 2022 to 6.9% this year, with 30-year-olds at 9.5%
- Age Disparities: Younger individuals have higher delinquency rates due to less stable incomes and higher debt-to-asset ratios, while older individuals have lower rates.
- Economic Stability: Overall economic indicators are stable with low unemployment, strong wages, robust GDP growth, and a strong stock market, despite rising delinquencies
- Emerging Strains: Financial stress is appearing among lower-income consumers and small businesses
- Market and Policy Implications: While markets remain confident, voter sentiment is impacted by rising costs and uneven economic gains, potentially affecting views on the administration's performance.
The chart depicts the percentage of total US credit card loans that are 90 days or more overdue, a metric known as serious delinquency. The data shows a notable increase in serious delinquencies, rising from 3% in Q1 2022 to 6.9% in the current year. Among 30-year-olds, the delinquency rate has reached 9.5%, approaching levels seen during the Global Financial Crisis (GFC).
In contrast, the delinquency rate for 60-year-olds remains much lower, illustrating a significant disparity between different age groups and highlighting underlying economic stresses.
Factors Behind the Trends
Several factors contribute to the higher delinquency rates among the younger population:
- Income Instability: Younger individuals often experience less stable income streams, making it harder to manage debt repayments consistently.
- Debt-to-Asset Ratios: Younger people typically have higher debt relative to their assets compared to older individuals, increasing their financial vulnerability.
- Economic Disparities: The current economic environment exacerbates these issues, with the spread between younger and aggregate delinquency rates reaching unprecedented levels.
Broader Economic Context
Despite the rise in credit card delinquencies, the overall economic outlook remains relatively stable. Key indicators suggest a robust economic environment:
- Household Debt: Total household debt as a percentage of GDP stands at 71%, significantly lower than the 98% peak during the Global Financial Crisis (GFC)
- Unemployment: Unemployment rates are at multi-decade lows, indicating a strong labor market.
- Wages and GDP Growth: Wages have remained strong, and GDP growth has outpaced other G7 countries since the pandemic.
- Stock Market Performance: The stock market continues to thrive, reflecting investor confidence.
These factors, coupled with savings accumulated during the pandemic, have allowed many consumers to manage rising living costs without significant stress. However, there are emerging signs of strain, particularly among lower-income consumers and small businesses.
Emerging Concerns
Recent trends indicate that the benefits of a strong economy are not being evenly distributed:
- Income Disparity: Lower-income consumers are beginning to show signs of financial distress.
- Small Business Adjustments: Small businesses are scaling back hiring plans, suggesting that the effects of higher interest rates and inflation are starting to impact economic activity
Implications for Markets and Policy
For financial markets, the current focus remains on the broader health of the economy, which appears stable. However, if key indicators like labor market strength or economic growth were to deteriorate significantly, concerns could escalate.
For policymakers and voters, the situation is more nuanced. Despite positive economic headlines, many individuals feel the strain of rising costs and uneven economic gains. This sentiment could influence public perception of the economic success of the current administration, particularly in the context of upcoming elections.
In summary, while the rise in credit card delinquencies signals potential economic challenges, the overall economic environment remains resilient. Continued monitoring of economic indicators and addressing income disparities will be crucial for maintaining stability and public confidence.
Source: Momentum Global Investment Management, Federal Reserve of New York, Q1 2024 Report on Household Debt and Credit.